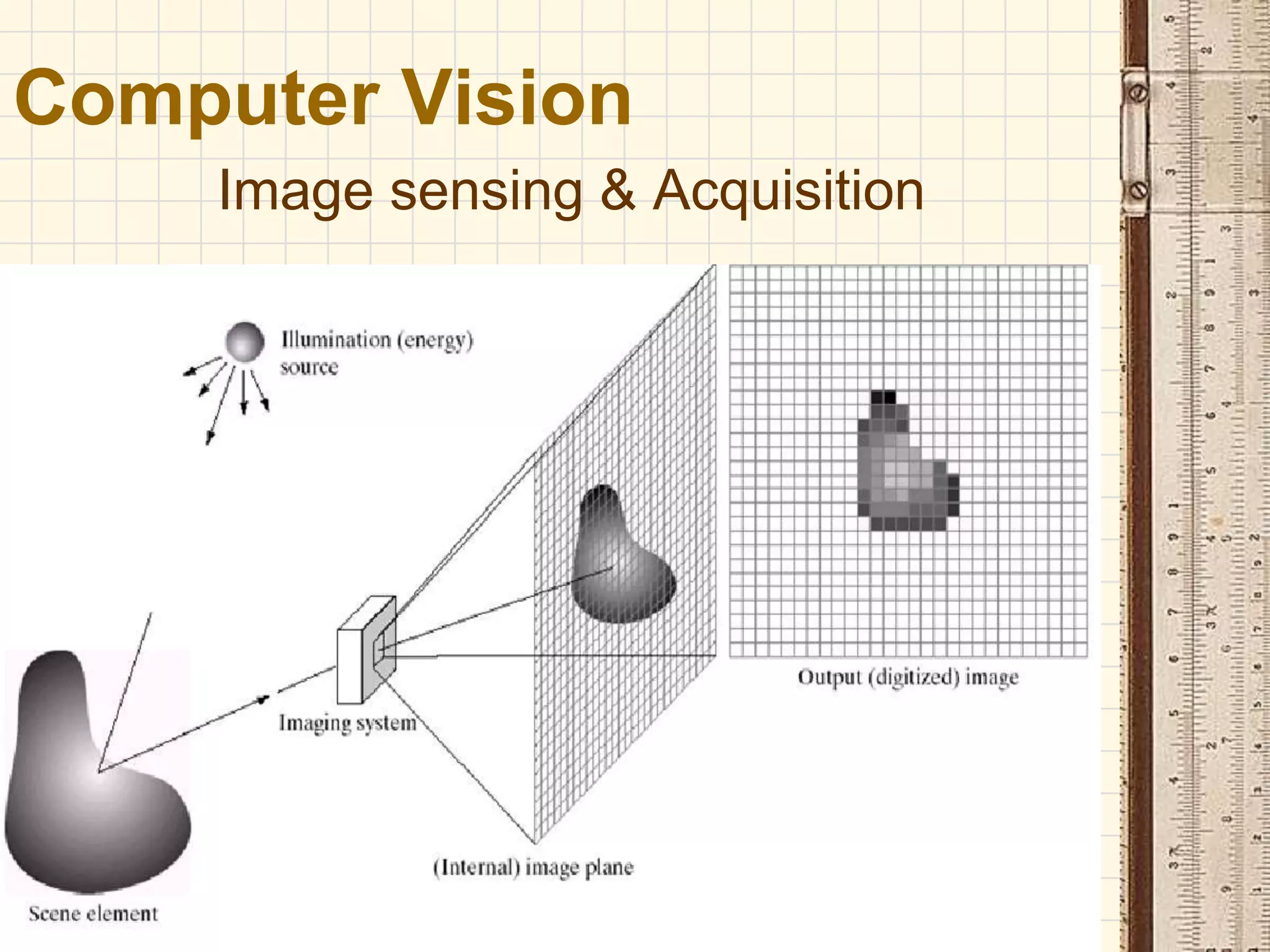
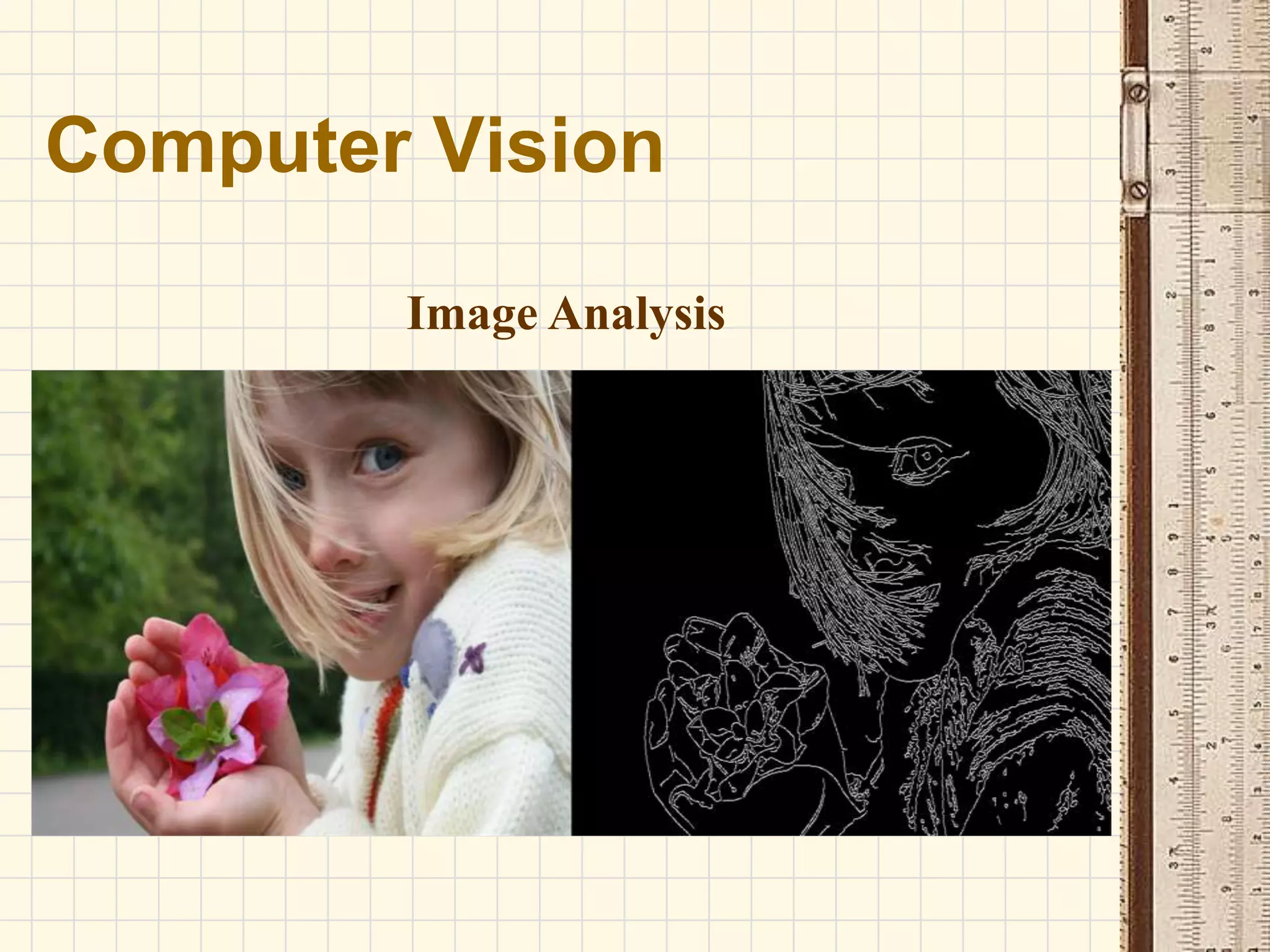
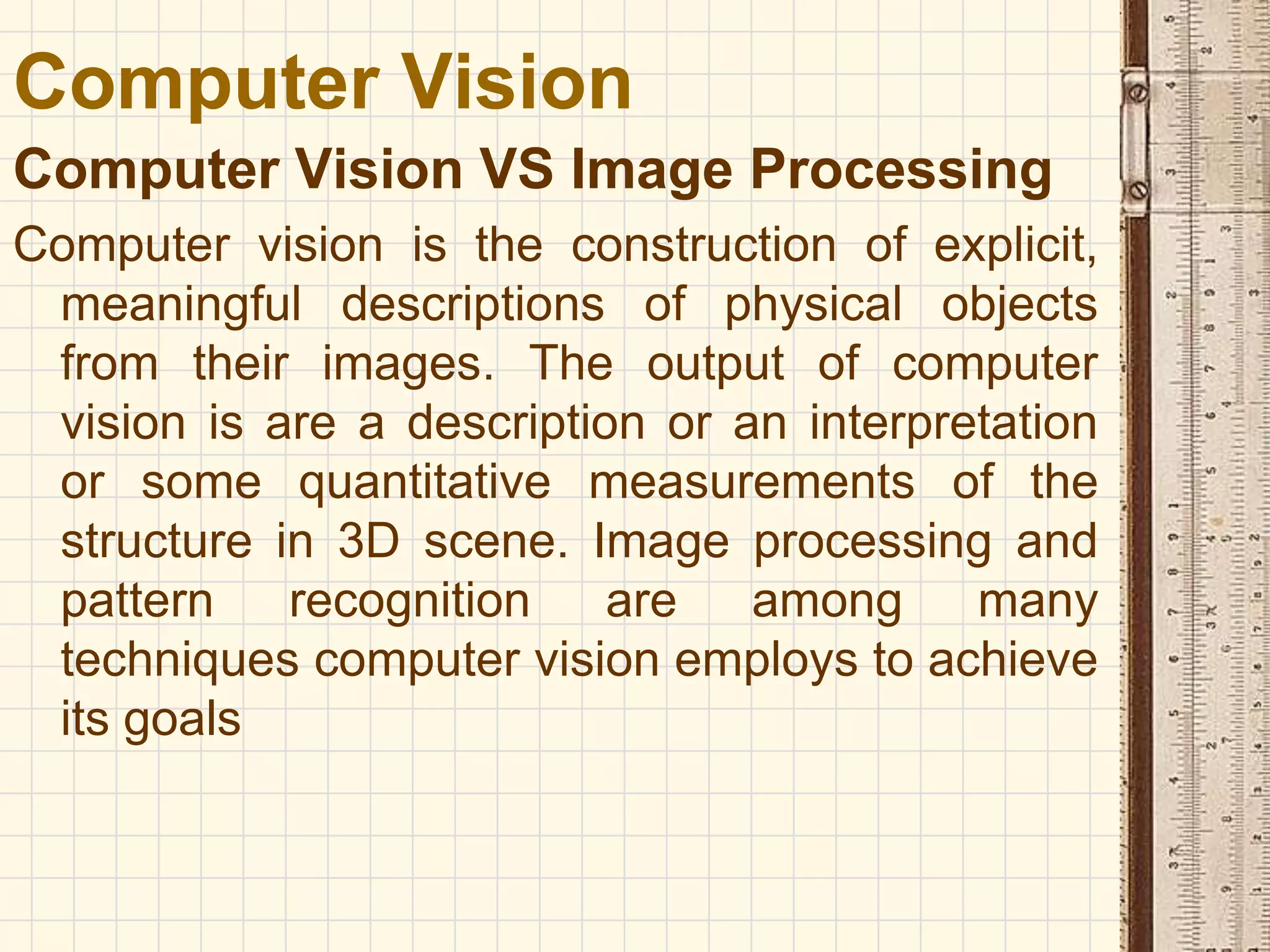
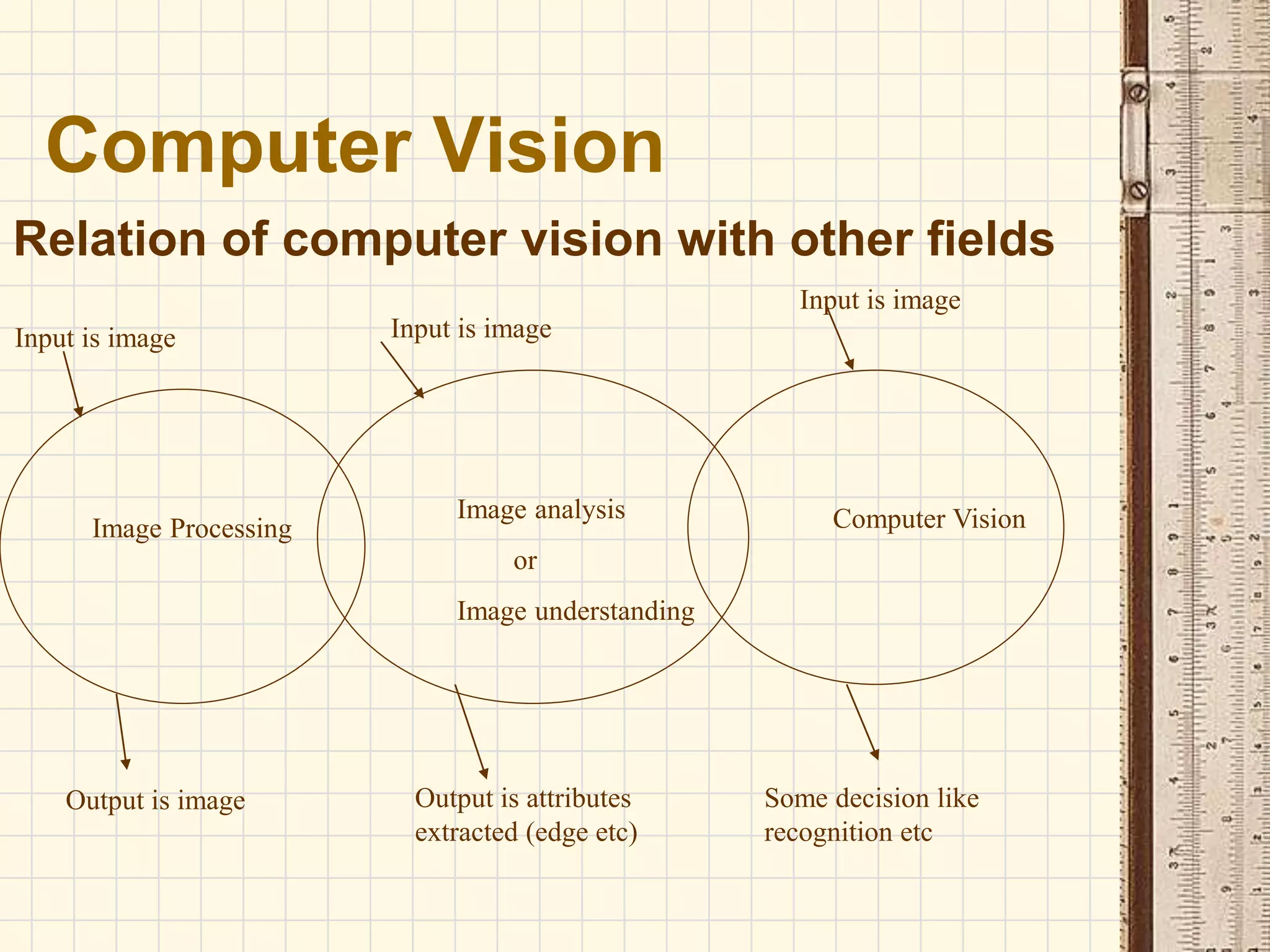
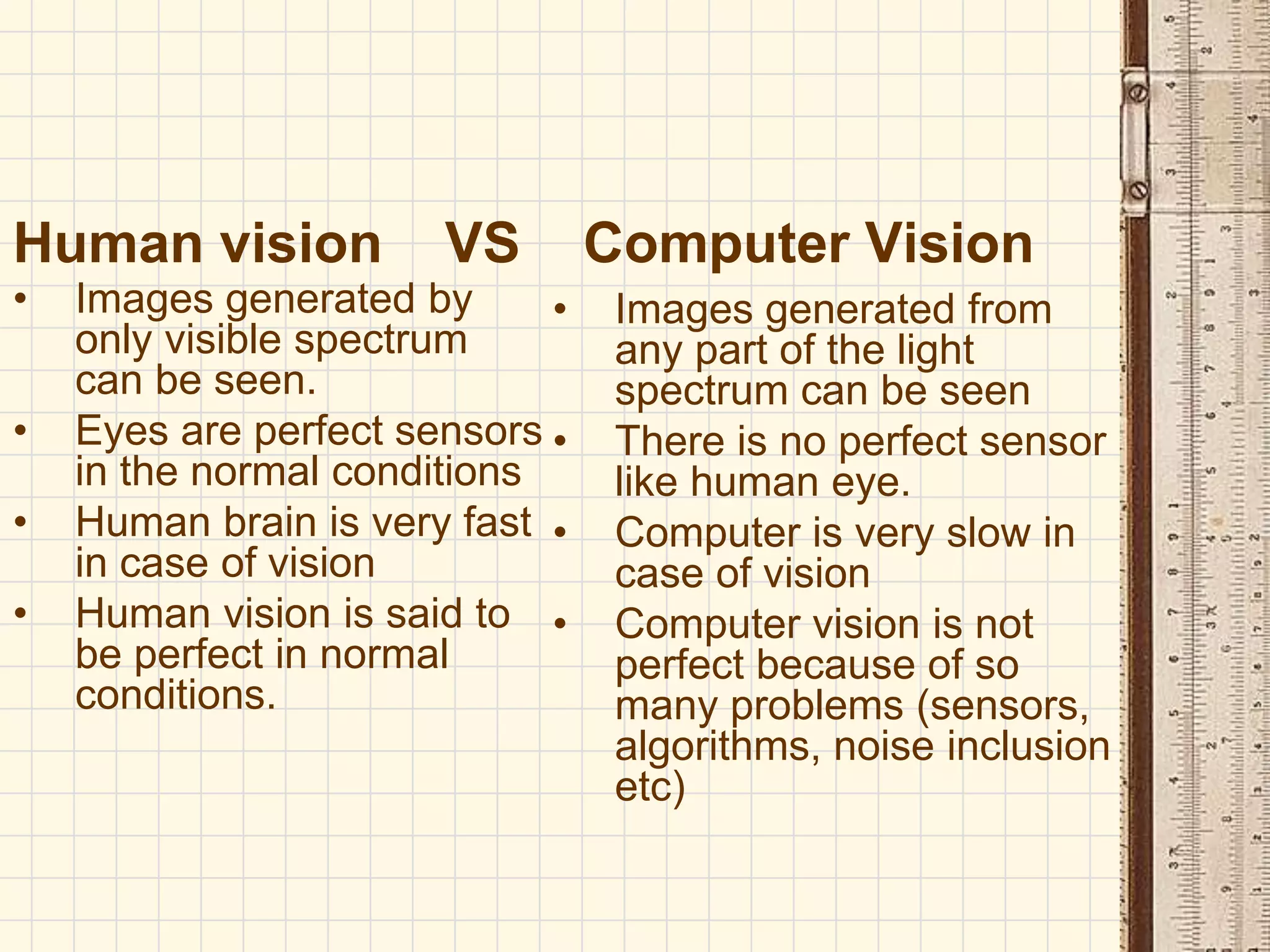
Computer vision is a field that uses methods to process, analyze and understand images and visual data from the real world in order to produce decisions or symbolic information. The goal of computer vision is to automatically extract, analyze and understand useful information from single images or sequences of images to represent real-world objects, similar to how humans use their eyes and brain for vision. Computer vision involves image acquisition, processing, analysis, and comprehension stages to sense images, improve image quality, examine scenes to identify features, and understand objects and their relationships.