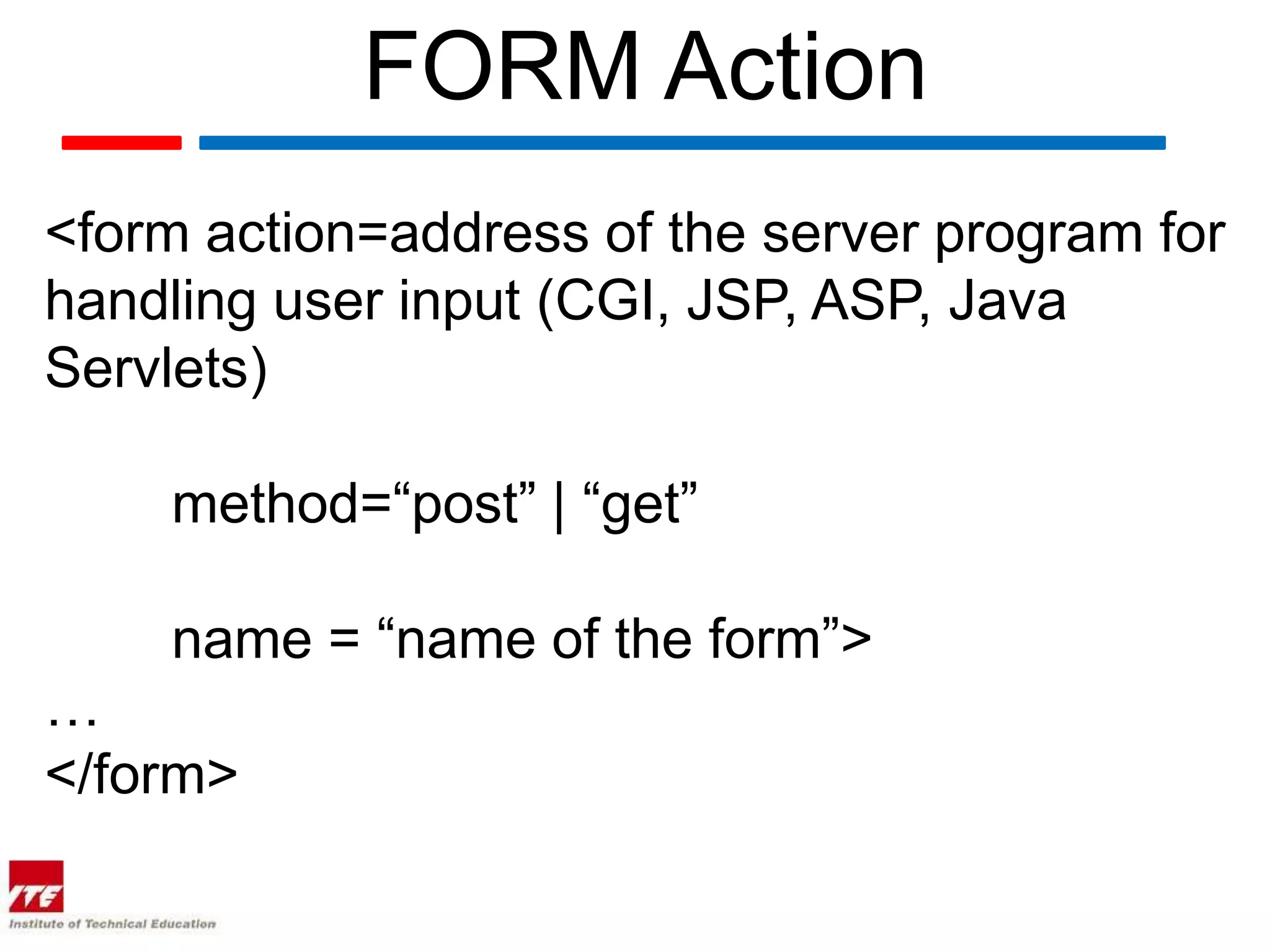
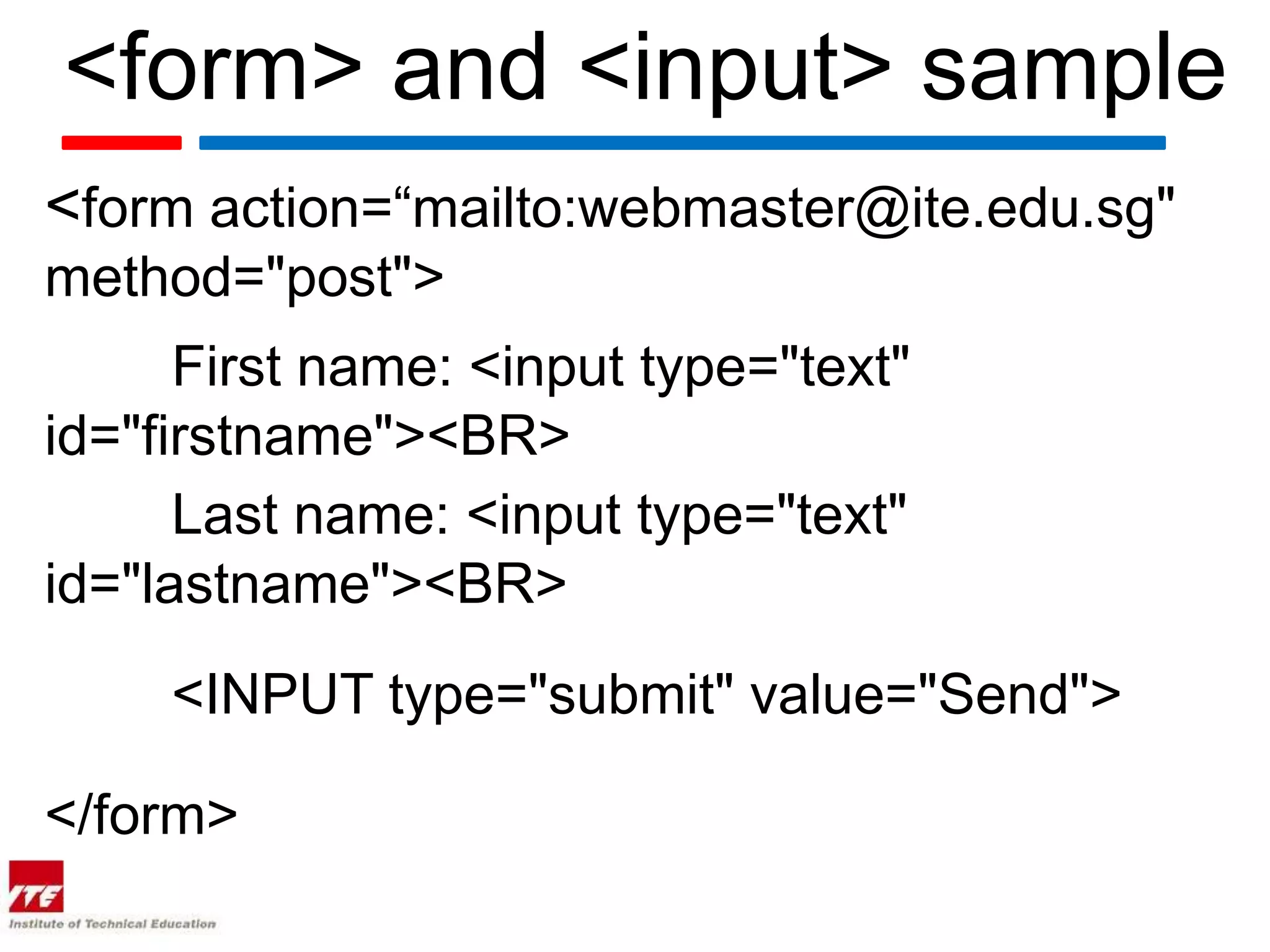
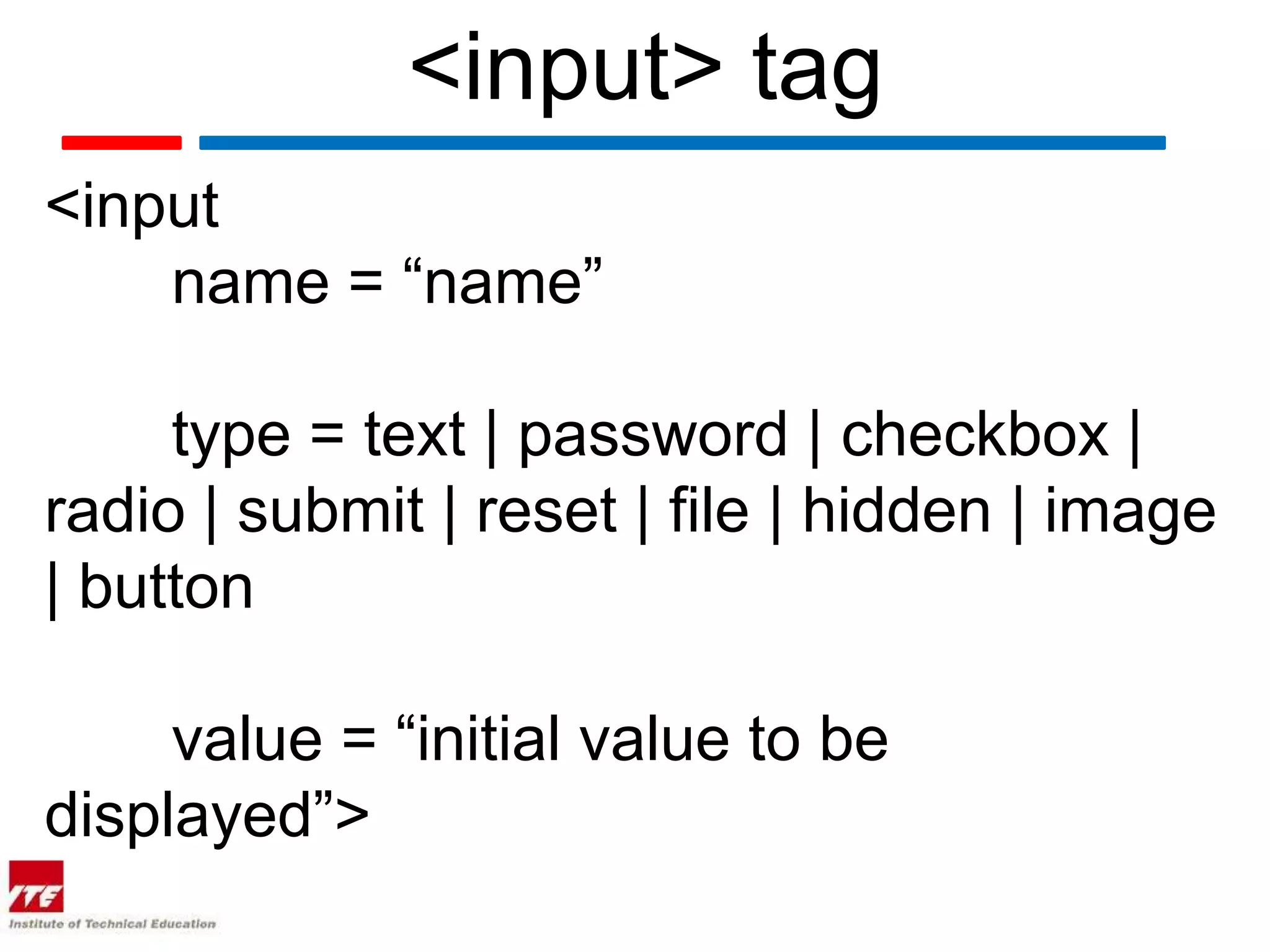
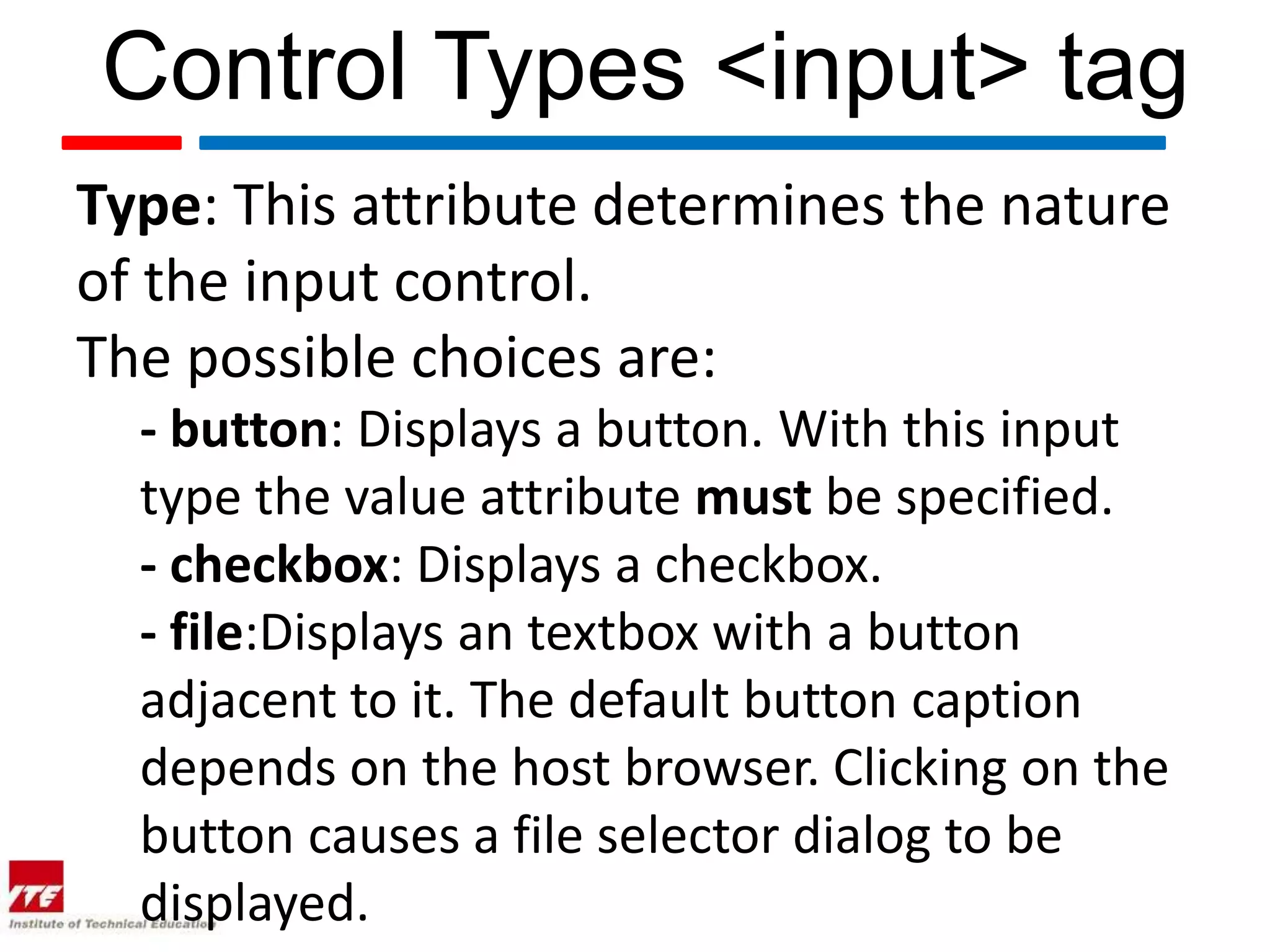
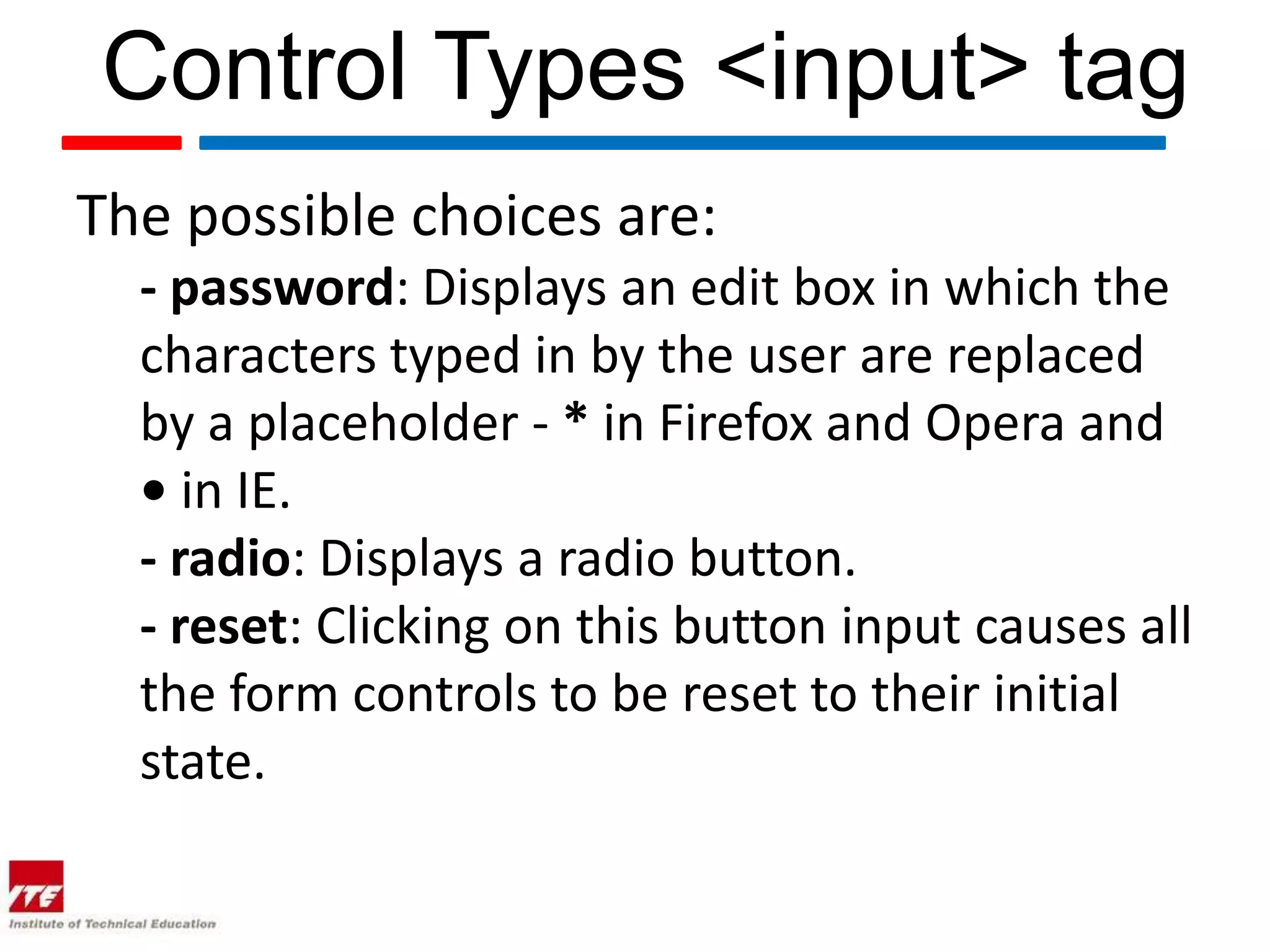
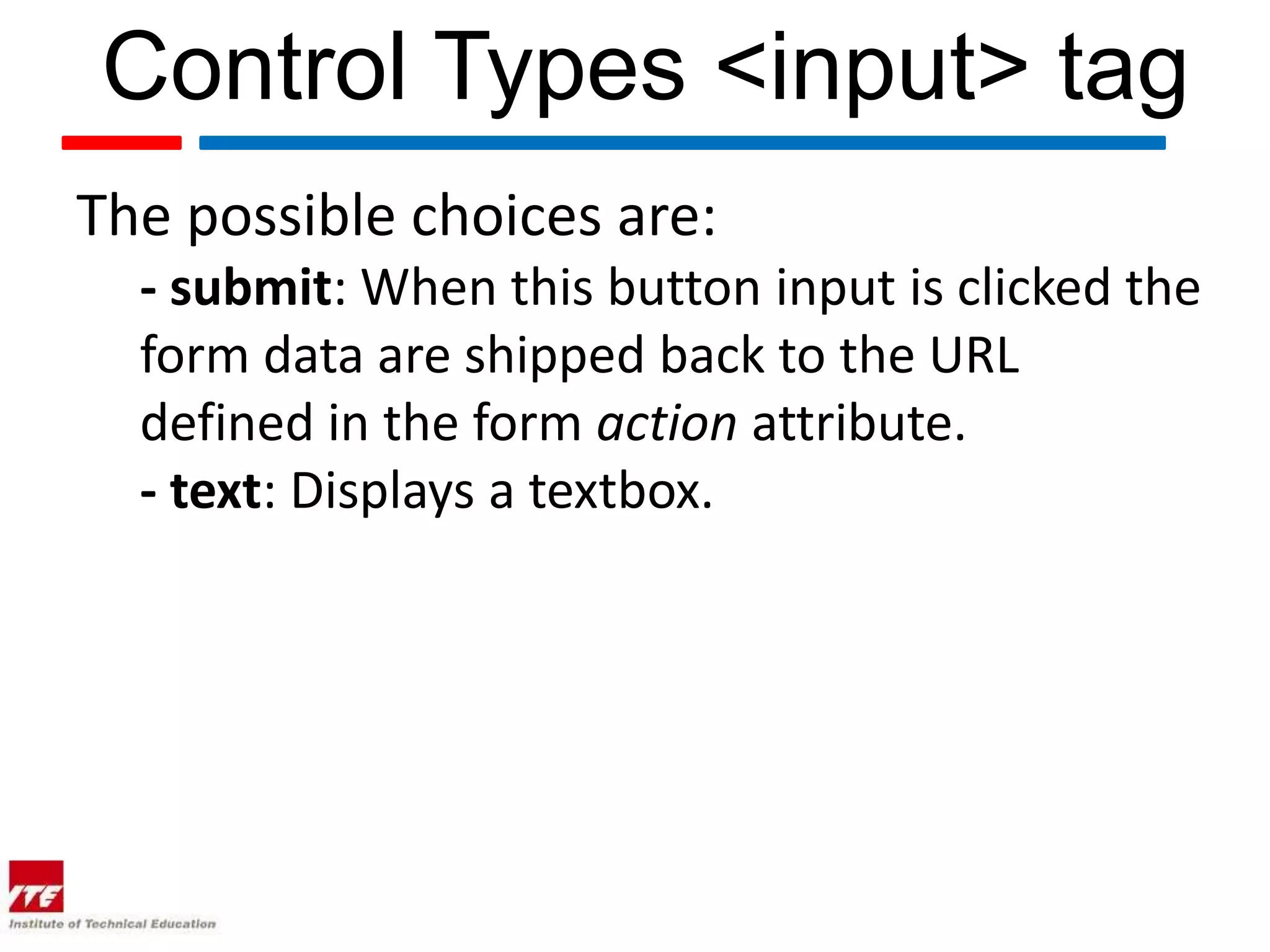
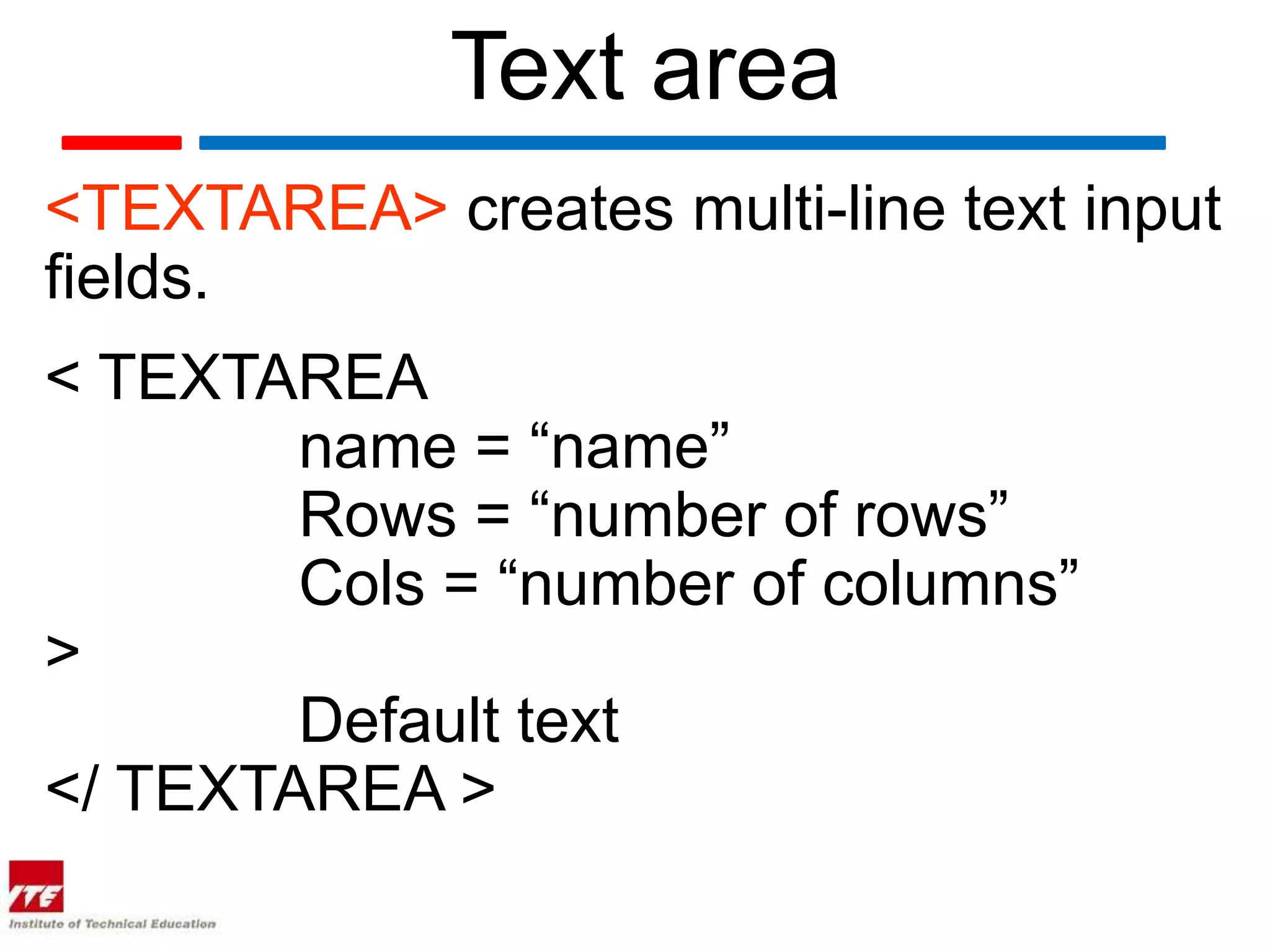
This document discusses HTML forms and the various form elements used to gather user input. It identifies the <form> tag which defines a form section and includes attributes like action and method. The <input> tag is used to create form controls like text boxes, checkboxes, radio buttons, etc. Other tags covered are <textarea> for multi-line text, <select> and <option> for drop-down menus, and <submit> for submitting the form. The document provides examples of how to use these tags to build interactive forms.







![Sample for <select>
<select
name = “name”
size = “size number”
multiple>
<option [selected]>option 1
<option [selected]>option 2
</select>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webtopic202-htmlforms-130409230139-phpapp01/75/Web-topic-20-2-html-forms-15-2048.jpg)
