Restoration of the unfolded protein response in pancreatic β cells protects mice against type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24225943
- PMCID: PMC4169117
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006534
Restoration of the unfolded protein response in pancreatic β cells protects mice against type 1 diabetes
Erratum in
- Sci Transl Med. 2013 Dec 4;5(214):214er11. Ngyuen, Truc [corrected to Nguyen, Truc]
Abstract
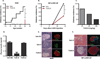
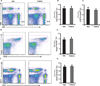
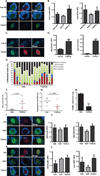
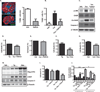
Perturbations in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis can evoke stress responses leading to aberrant glucose and lipid metabolism. ER dysfunction is linked to inflammatory disorders, but its role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D) remains unknown. We identified defects in the expression of unfolded protein response (UPR) mediators ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) and XBP1 (X-box binding protein 1) in β cells from two different T1D mouse models and then demonstrated similar defects in pancreatic β cells from T1D patients. Administration of a chemical ER stress mitigator, tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), at the prediabetic stage resulted in a marked reduction of diabetes incidence in the T1D mouse models. This reduction was accompanied by (i) a significant decrease in aggressive lymphocytic infiltration in the pancreas, (ii) improved survival and morphology of β cells, (iii) reduced β cell apoptosis, (iv) preserved insulin secretion, and (v) restored expression of UPR mediators. TUDCA's actions were dependent on ATF6 and were lost in mice with β cell-specific deletion of ATF6. These data indicate that proper maintenance of the UPR is essential for the preservation of β cells and that defects in this process can be chemically restored for preventive or therapeutic interventions in T1D.
Figures


Comment in
-
Diabetes: Targeting endoplasmic reticulum to combat juvenile diabetes.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014 Mar;10(3):129-30. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.261. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24393784 Free PMC article.
-
From immunobiology to β-cell biology: the changing perspective on type 1 diabetes.Islets. 2014;6(2):e28778. doi: 10.4161/isl.28778. Islets. 2014. PMID: 25483958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A. Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010;10:501–513. - PubMed
-
- Mathis D, Vence L, Benoist C. β-Cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature. 2001;414:792–798. - PubMed
-
- van Belle TL, Coppieters KT, von Herrath MG. Type 1 diabetes: Etiology immunology and therapeutic strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2011;91:79–118. - PubMed
-
- Eizirik DL, L Colli M, Ortis F. The role of inflammation in insulitis and β-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009;5:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Todd DJ, Lee AH, Glimcher LH. The endoplasmic reticulum stress response in immunity and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008;8:663–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

