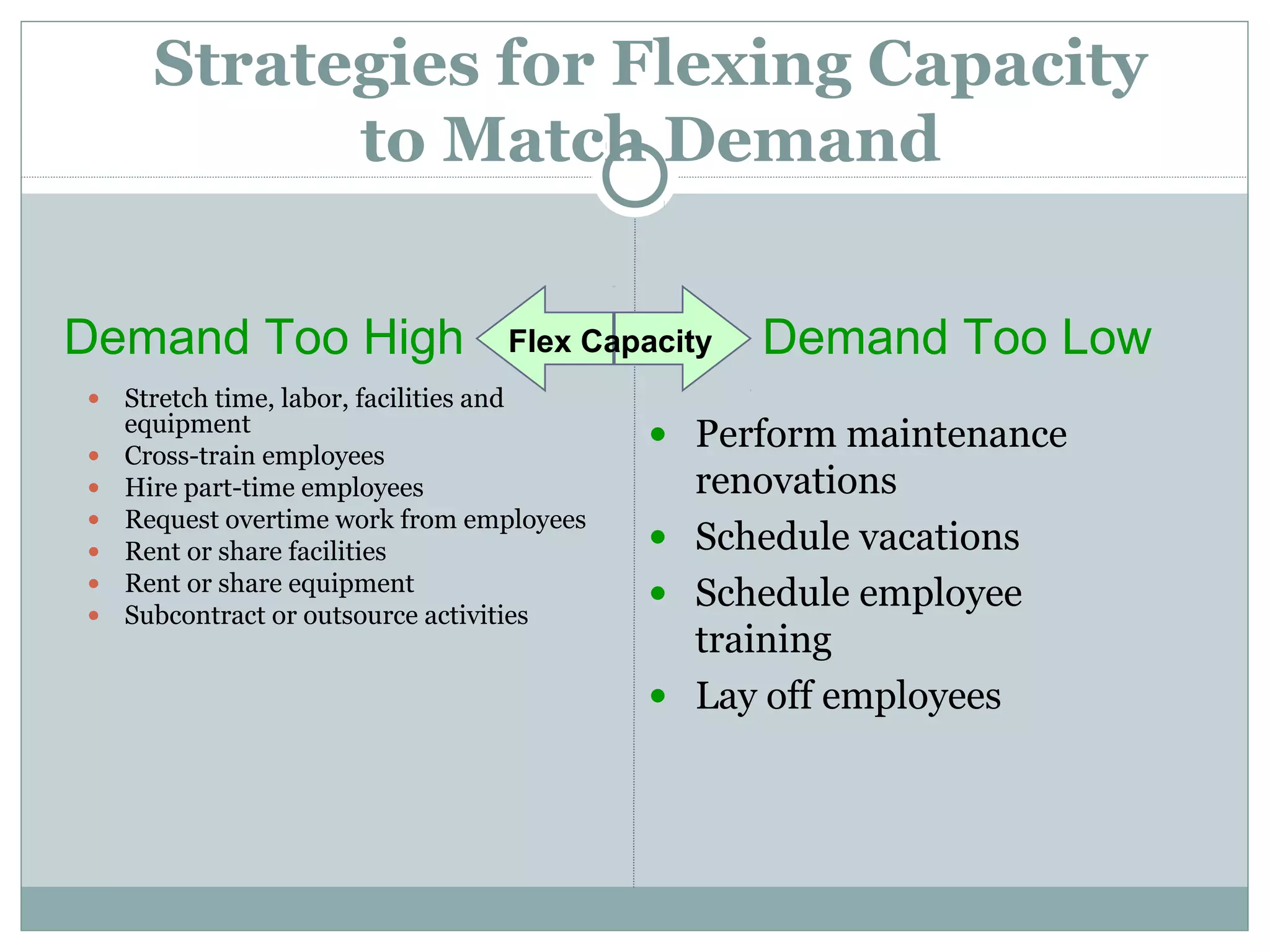
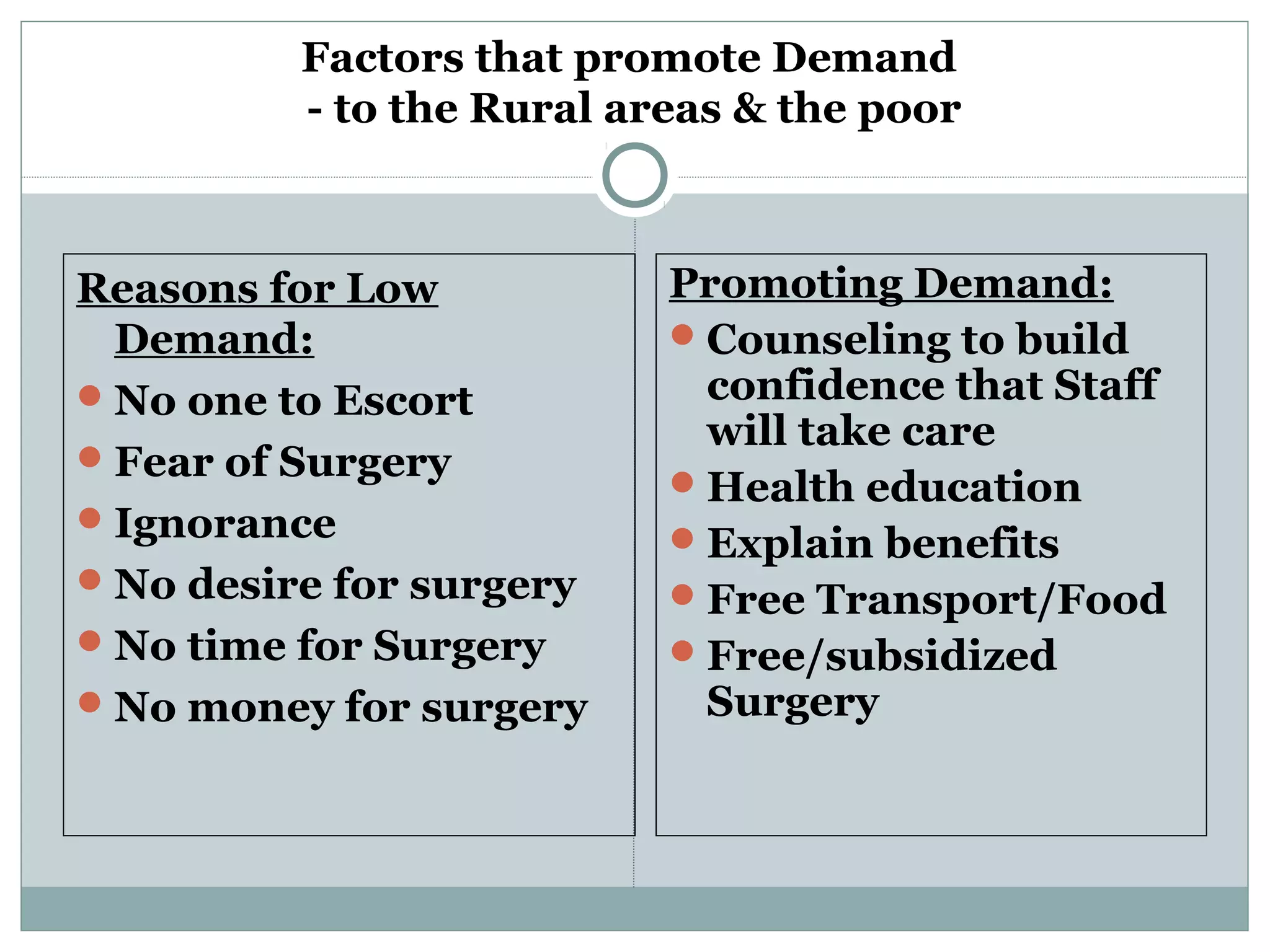
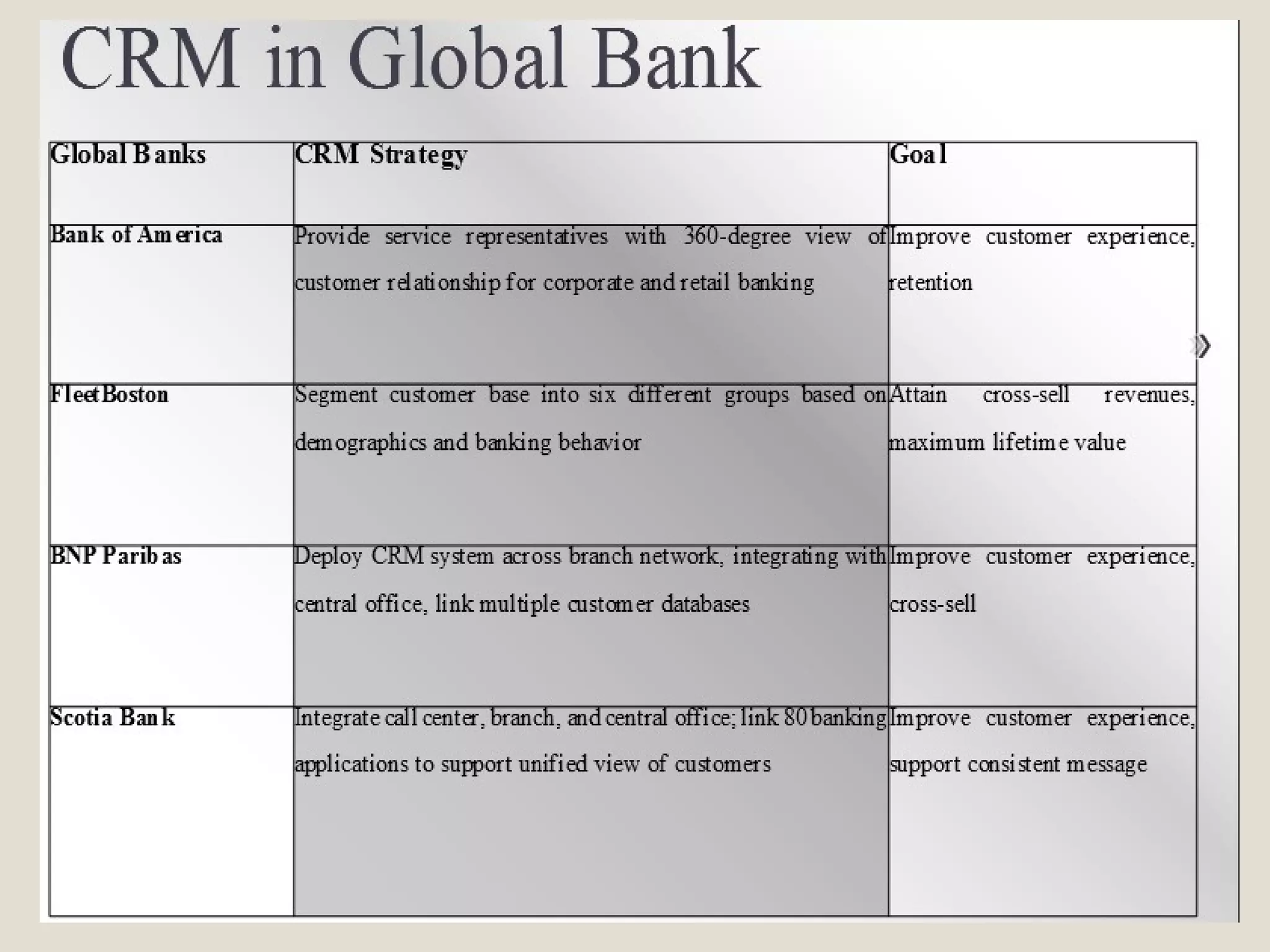
The document discusses strategies for matching supply and demand in service industries. It explains the underlying issues of capacity constraints for services and the implications of different demand patterns on balancing supply and capacity. The key strategies proposed are shifting demand to match capacity by changing pricing and promotions, or flexing capacity to meet demand by adjusting staffing levels and outsourcing. Yield management strategies are also covered. The benefits and risks of different approaches are outlined. Customer relationship management and its focus on customer retention over just acquisition is also briefly defined.