Ask or search anything...
What are the most popular benchmarks for math reasoning?
Researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and collaborators developed SKILLRL, a framework enabling Large Language Model (LLM) agents to learn and recursively evolve abstract skills from diverse experiences. SKILLRL achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 89.9% success rate on ALFWorld, 72.7% on WebShop, and an average score of 47.1% on search-augmented QA tasks, outperforming larger closed-source models and memory-augmented baselines.
View blogThe Agent World Model (AWM) introduces a pipeline to synthesize 1,000 diverse and reliable interactive environments for training large language model (LLM)-powered agents. Agents trained on these code-driven, database-backed environments from Snowflake and UNC showed strong generalization to unseen real-world tool-use benchmarks.
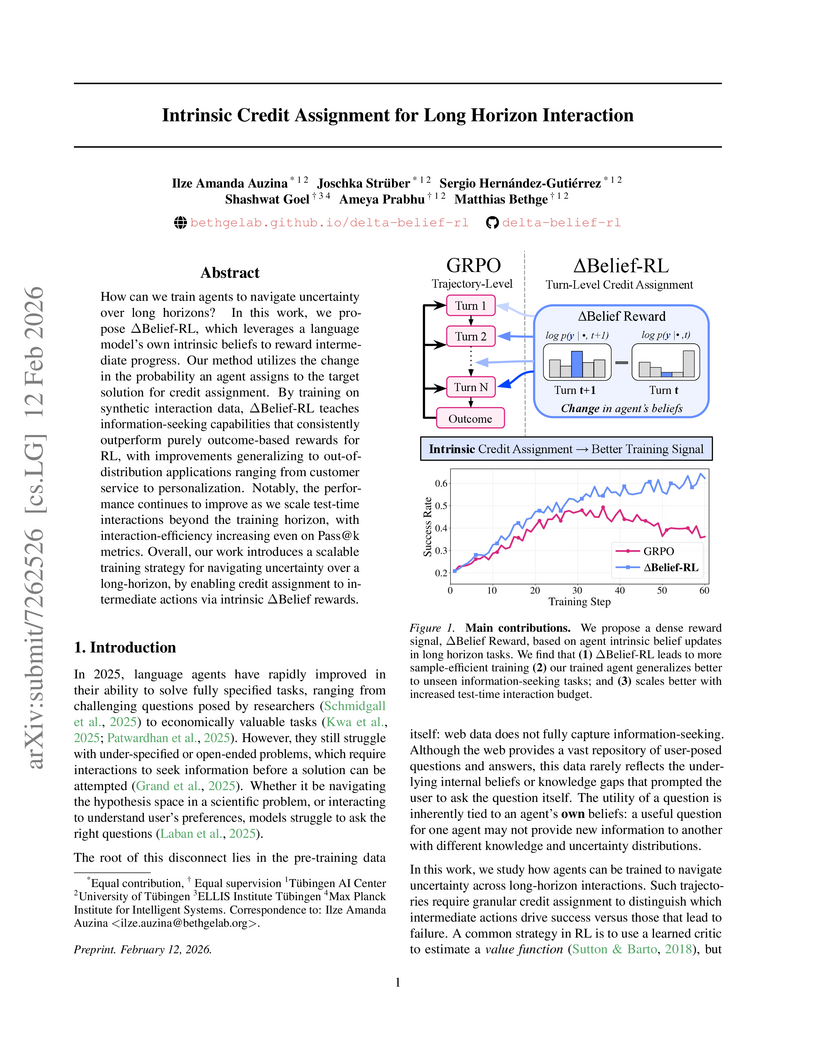
View blogResearchers at the University of Tübingen developed the "Intrinsic Credit Assignment for Long Horizon Interaction" (ΔBelief-RL) framework, which trains agents by using their own internal belief changes as a dense, per-turn reward signal. This approach allowed smaller models to significantly outperform larger general-purpose LLMs and state-of-the-art baselines in active information-seeking tasks, demonstrating enhanced efficiency and strong generalization across various interactive environments.
View blogOn-Policy Context Distillation (OPCD) enables language models to internalize transient in-context knowledge by training student models on their own generations guided by a context-conditioned teacher using reverse KL divergence. This approach yields improved task accuracy, better out-of-distribution generalization, and effective knowledge transfer across model sizes, overcoming limitations of off-policy distillation.
View blogVLA-JEPA integrates a leakage-free latent world model, inspired by JEPA, into a Vision-Language-Action framework for robust robotic control. This approach yields state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks like LIBERO and enhanced robustness in perturbed environments, effectively utilizing human videos to impart common-sense skills such as "repeated grasping."
View blogResearchers at Johns Hopkins University introduce ViT-5, a modernized Vision Transformer architecture that systematically incorporates architectural advancements from Large Language Models, yielding improved performance across image classification, generation, and dense prediction tasks. ViT-5-Base achieved 84.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1k, surpassing DeiT-III-Base, and reduced FID to 1.84 in image generation compared to 2.06 for a vanilla ViT backbone.
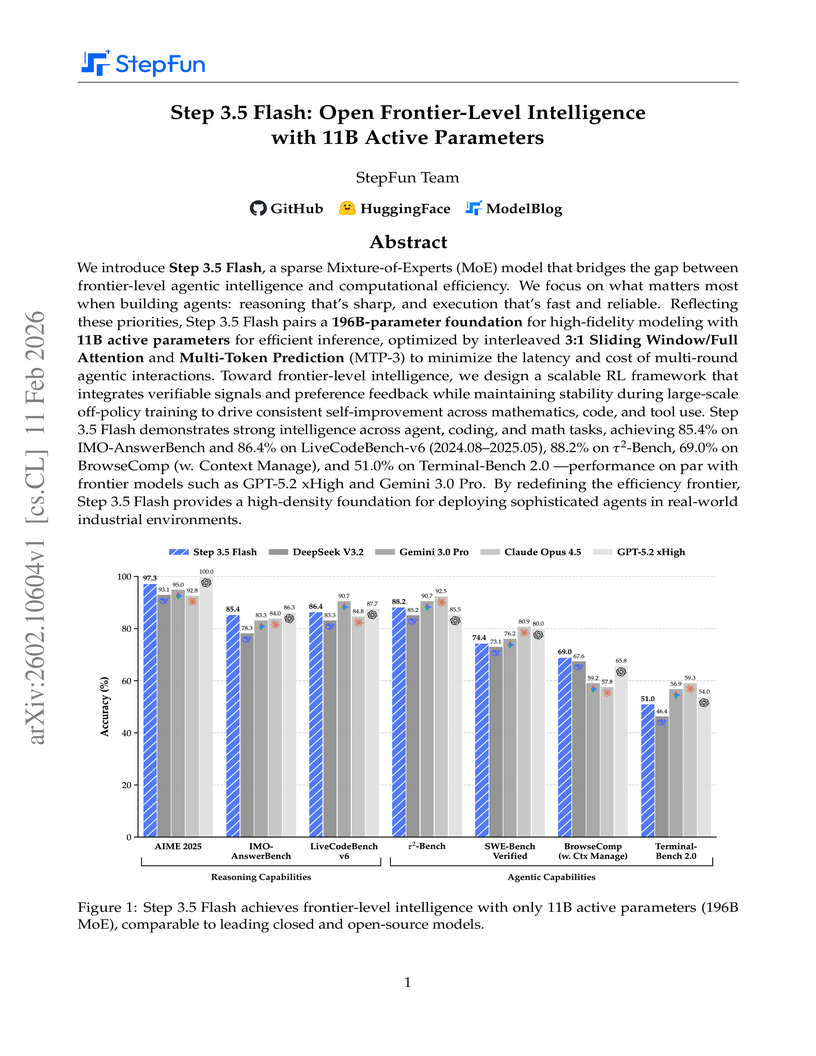
View blogStep 3.5 Flash is an 11B active parameter model, built upon a 196B total parameter Mixture-of-Experts architecture, that demonstrates intelligence on par with leading proprietary frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. It achieves superior capability density and efficiency for long-context agentic tasks across reasoning, coding, and tool use, sustaining approximately 170 tokens/s during real-world deployment.
View blogGigaBrain-0.5M* integrates world model-based reinforcement learning into a Vision-Language-Action model, enabling enhanced robotic manipulation for complex, long-horizon tasks. This approach achieves near-perfect success rates on challenging real-world tasks and secured a top position on the RoboChallenge benchmark leaderboard.
View blogTHINKROUTER introduces a training-free inference mechanism that dynamically routes Large Reasoning Models between discrete token and latent reasoning spaces based on real-time confidence. This approach improves Pass@1 accuracy by up to 19.70 points and reduces generation length by 4.56% to 10.78% on STEM tasks, mitigating noise propagation and overconfidence in latent reasoning.
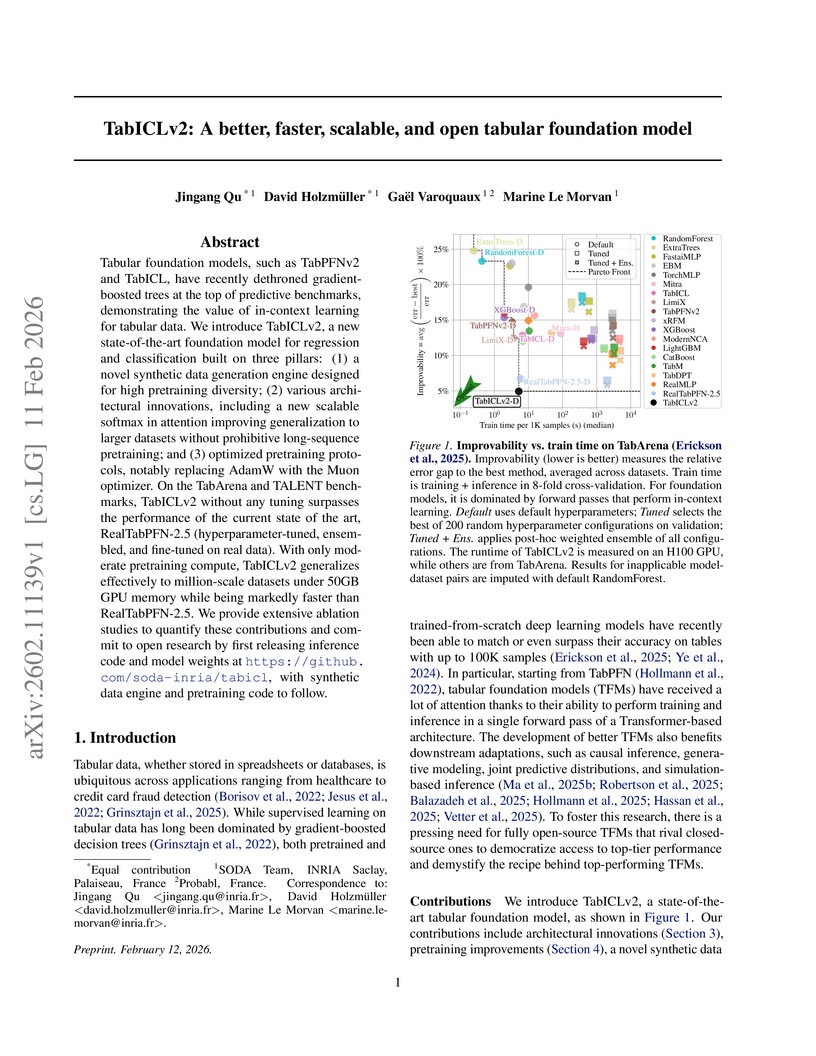
View blogResearchers at INRIA Saclay introduced TabICLv2, a tabular foundation model that achieves state-of-the-art predictive performance on benchmarks like TabArena and TALENT, outperforming tuned models such as RealTabPFN-2.5 by an average rank of 4.82 vs 5.88 and 4.66 vs 5.11 respectively. The model is significantly faster, showing 10.6x speedup on H100 GPUs, and offers native scalability to million-sample tables through disk offloading, all while being fully open-source.
View blogMakora researchers fine-tuned GPT-5 using a Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) framework to generate highly optimized Triton GPU kernels. Their fine-tuned model (GPT-5-RL) achieved 77.0% functional correctness and outperformed PyTorch's TorchInductor on 21.8% of problems in a single attempt, with their `MakoraGenerate` agent reaching 97.4% correctness and a 2.12x geometric mean speedup over TorchInductor.
View blogResearchers introduce Code2World, a GUI world model that predicts future UI states by generating renderable HTML code from current observations and actions. This model provides autonomous GUI agents with foresight, substantially improving their navigation accuracy and task success rates by enabling them to simulate action consequences.
View blogPhyCritic introduces a multimodal critic model trained with a two-stage Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) pipeline, leveraging self-referential finetuning to enhance its ability to evaluate and reason about physical AI tasks. The model achieves 68.0% accuracy on the new PhyCritic-Bench for physical judgment, outperforming existing open-source models by over 12 percentage points, and also improves the base model's physical reasoning capabilities.
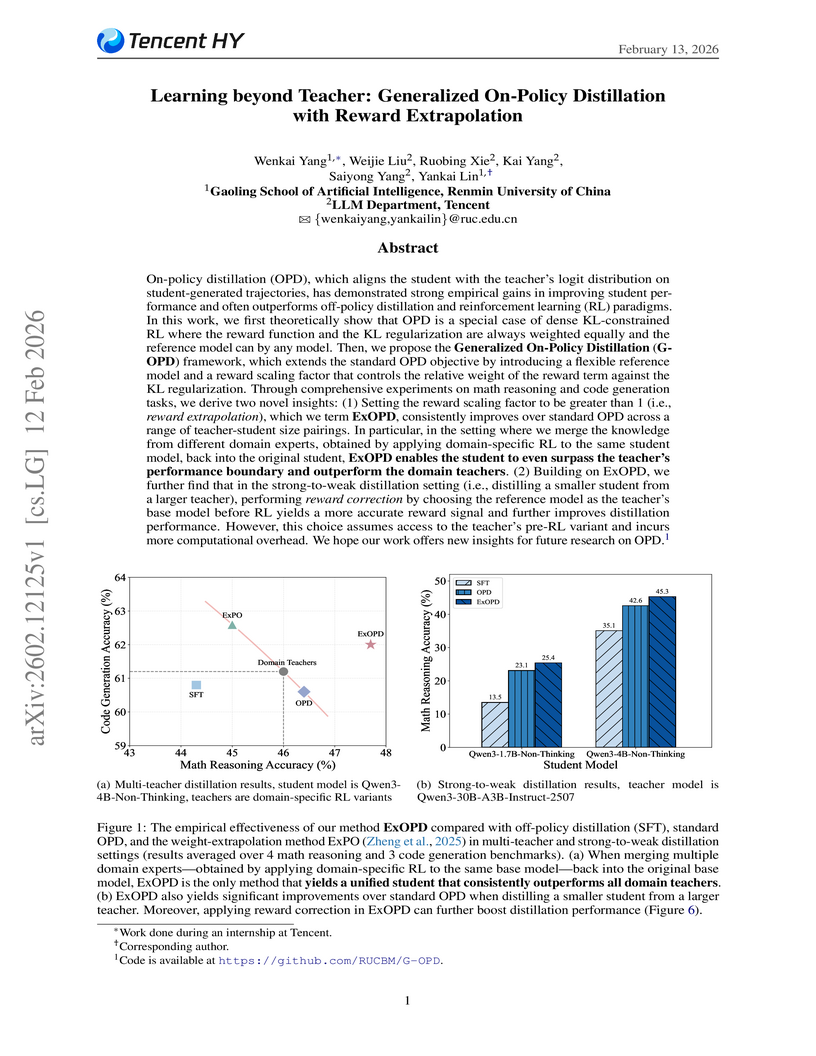
View blogResearchers from Renmin University and Tencent introduced Generalized On-Policy Distillation (G-OPD) with its reward extrapolation variant (ExOPD), which allows student large language models to surpass teacher performance and effectively merge capabilities from multiple expert teachers. The method achieved performance improvements, including a +2.7% gain in strong-to-weak distillation over standard on-policy methods.
View blogThe OneVision-Encoder framework introduces a codec-aligned sparsity principle for visual representation learning, drawing inspiration from video compression, to selectively process information-rich visual regions. This approach delivers superior performance across image, video, and document understanding benchmarks, requiring substantially fewer pretraining tokens while reducing patch processing by 75.0%-96.9% compared to dense baselines.
View blogSoftMatcha 2, a pattern matcher for trillion-scale text corpora, enables fast, semantically flexible search by handling word substitutions, insertions, and deletions while preserving word order. On the 1.4T token FineWeb-Edu corpus, it achieves sub-second search times (p95 latency of 278.17 ms) and effectively detects subtle benchmark contamination in LLM training data with 81% precision for newly found cases.
View blogGoodfire AI introduces Reinforcement Learning from Feature Rewards (RLFR), a method that leverages internal neural network features as scalable reward functions for Large Language Models. This approach led to a 58% reduction in hallucinations in a Gemma-3-12B-IT model and reduced reward computation costs by approximately 90x during training.
View blogLatent Forcing enhances pixel-space image generation by concurrently diffusing semantic latent representations and raw pixels, using independent noise schedules to prioritize high-level structure. This approach enables state-of-the-art performance for Diffusion Transformers on ImageNet 256x256 while preserving lossless image reconstruction.
View blogResearchers from Alibaba Group's AMAP CV Lab developed ABot-M0, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) foundation model that leverages a systematically harmonized dataset of over 6 million trajectories and a novel Action Manifold Learning paradigm to achieve state-of-the-art performance across diverse robotic manipulation benchmarks, including an average 98.6% success rate on LIBERO.
View blog University of Chicago
University of Chicago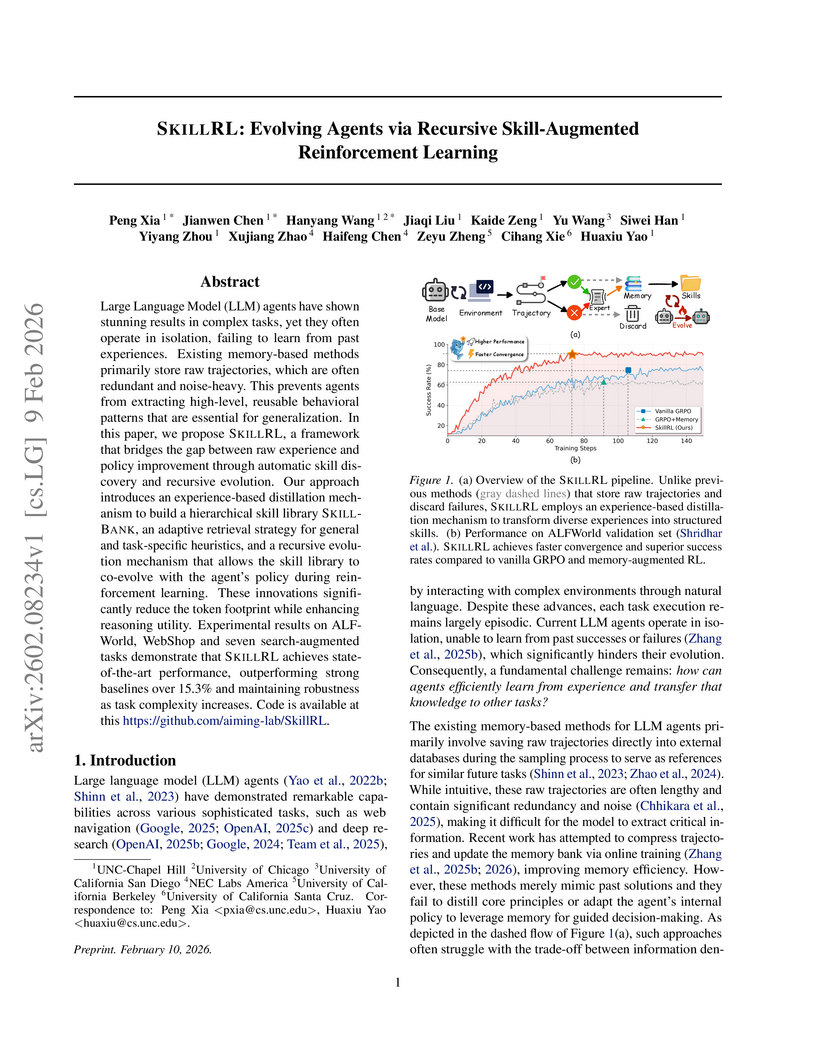


 Microsoft
Microsoft

 Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University University of California, Santa Cruz
University of California, Santa Cruz

 University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Adobe
Adobe

 Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Oxford
University of Oxford
 University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park NVIDIA
NVIDIA



 Stanford University
Stanford University University of Michigan
University of Michigan
 Alibaba Group
Alibaba Group